May 15, 2024
WASTE POLLUTION
DEFINITION OF WASTE
The waste is often identified as the solid waste that is deposited in landfills. However, it is a much broader concept, and it has great consequences for humans, animals, plants, and the environment. The pollution it produces is one of the main problems we have to deal with.
It is all the waste produced by humans that has not been managed in an appropriate way so that it is not reintroduced into the environment or other human activities. It is physical objects that accumulate in landfills, in cities or in nature. Considering that they are also the chemical substances that these objects release and that mix with the environment, be it land, water or air, and consequently pollute it.
CAUSES
The main cause of waste pollution is poor waste management. We must take into in mind that waste is not the material, but the way it is managed. For example, a piece of paper will be waste or raw material depending on how it is managed. If it ends up in the environment it will be waste, but if it is deposited in a recycling container, it will become raw material.
EDUCATING HUMAN -> CHANGING HUMAN BEHAVIOR
5 Countries That Produce the Most Waste
Countries around the globe continue to generate large amounts of waste as their populations grow and economies expand. As of 2022, the World Bank estimated that waste generation will increase as much as 70%—from 2.01 billion tonnes to 3.40 billion in 2050.
The Global Waste Index is a comprehensive analysis that ranked 38 member states of the Organization for Economic Cooperation and Development (OECD) according to the environmental impact of their waste management in 2022. Factors considered included the amount of waste generated, recycling, incineration, landfill, and illegal dumping. In 2022, Turkey topped the countries with the worst waste management.
1. Turkey
Turkey ranks first with the least environmentally proactive waste management programs. In 2019, Turkey did not have a recycling option. Although recycling has increased to 47kg per capita in 2022, close to 176kg of waste per capita is unaccounted for and illegally disposed of annually.
2. Latvia
Latvia ranks second in 2022, with over 32% of waste unaccounted for and outside landfills and recycling programs.
In 2021, Latvia implemented a long-term strategy and waste management plan through 2028. It aims to establish an infrastructure for the collection of goods and the creation of centers for recycling.
3. Chile
Chile ranks third and is the country that recycles the least at only two kilos per inhabitant. 417kg of waste per capita is disposed of in a landfill, and 33kg in an open dump. Waste Management World. "Global Waste Index."
In September 2023, the Chilean government implemented the Extended Producer Responsibility Law mandating manufacturers or importers to recycle oil & lubricants, electronic devices, industrial or vehicle batteries, small batteries, packaging materials and containers, and tires. The country aims to improve recycling, reduction, and reutilization of solid waste by 2040.
4. Mexico
In 2022, Mexico did not have an incineration program for waste management. Mexico City is the second biggest waste producer among the world’s cities, behind New York City, generating 20,000 tons daily. However, the waste is only disposed of in landfills.
5. Italy
Although Italy implemented the National Recovery and Resilience Plan, also known as the NRRP, in 2022, the country remains the fifth largest waste producer. The NRRP provides 2.10 billion euros to make waste management more efficient and sustainable and promote a circular economy in Italy.
Countries with the most efficient efforts at minimizing waste
1. Switzerland have 100% waste recovery, despite being in the top five for waste production (only behind Netherlands, Denmark and the USA). Switzerland stopped burying rubbish in landfills in 2000, and now they recover 53% of their waste through material recovery (i.e. recycling and composting), while the other 47% is incinerated for energy.
2. Sweden are also extremely close to fully recovering their waste at 99%. They are in the top five recyclers at 32%, with composting efforts at 16% of total waste. They recover more even more energy through incineration than Switzerland do at 52%. In fact, their municipal waste is generated into heat within their 35 waste-to-energy powerplants; heating the homes, power buses and taxis of its 10 million residents.
3. Denmark are also high at 99%, putting two Nordic countries in the top. Denmark fall slightly below Sweden for recycling (29%), but achieve slightly higher in composting (18%). Similar to Sweden, over half of their waste recovery comes from incineration at 53%. Despite their revolutionary waste management systems, however, Nordic nations still require a significant increase in recycling rates to meet the revised European Union (EU) recycling targets (of 65%) for 2035.
PANDAWA GROUP
Pandawara Group is the name of one group of Indonesian boys from Bandung, West Java. This group’s name started to be known by many people since they started cleaning up various rivers and beaches in several regions in Indonesia.
Pandawara Group have 5 members, named Gilang, Ikhsan, Rafly, Rifqi, and Agung. According to several sources, the grup has cleaned up 620 tons of waste in 187 places in many areas in Indonesia since 2022.


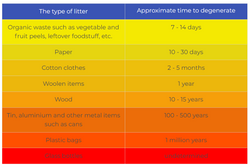
HOW TO RECYCLE
SOLID WASTE
Recycling refers to the reuse or recovery of materials that would normally be considered as waste. There are a few different methods of recycling such as: physical reprocessing, biological reprocessing, and energy recovery.
Recycling is good for the environment. It supports zero waste strategies and sustainability targets, reducing the amount of unrecoverable waste that is disposed of in landfill. Examples of solid waste that can be recycled include:
Paper and card, including mail, newspapers and magazines
Plastics
Aluminium and metal cans
Food packaging
Glass and ceramics
Inkjet cartridges and batteries
Bulbs
One of the most common methods of recycling is physical reprocessing. This is the method of taking waste materials and using the material to create new products.
ORGANIC WASTE
Materials such as plants, food scraps, and paper products can also be decomposed into organic matter. The organic matter that is produced from this type of recycling can then be used for things such as agricultural uses. Usually this method of recycling is done by putting the waste materials in a dedicated container until they decompose.
Waste to Energy
The final method of recycling is waste to energy recovery. Waste to energy (WtE) process involves the conversion of non-recyclable waste items into useable heat, electricity, or fuel through a variety of processes. This type of energy is a renewable energy source as non-recyclable waste can be used repeatedly to create it.
GENERAL WASTE
General waste is waste that is not hazardous, offensive, clinical or cannot be recycled. It is usually collected by local authorities or private businesses and the majority is then disposed of in landfill sites. There is a national waste strategy to reduce the amount of materials going to landfill through schemes such as reuse and recycle and education around the benefits of recycling.
General waste should always be disposed of correctly and safely. Waste is collected in black bins, placed in wheeled bins and skips to await collection. It is against the law to dispose of any hazardous waste within general waste.
HAZARDOUS WASTE
Hazardous waste includes all types of rubbish that are flammable, toxic, corrosive and reactive.
These items can harm you as well as the environment and must be disposed of correctly. Therefore, always use a reputable waste management company for proper disposal of all hazardous waste.
The four ways of disposing of hazardous waste are:
Recycling: A few hazardous wastes can be recycled to form other products. For example, circuit boards and lead-acid batteries can bind to other pollutants and later used as pavement fillings. Chemical levels are reduced when hazardous wastes are converted to new products.
Incineration and Destruction: Another way of disposing of hazardous waste is to destroy or incinerate them. Incineration reduces the amount of hazardous waste and can also generate energy for use in the process.
Pyrolysis: Pyrolysis, in a very high-temperature and under inert conditions, is an excellent way to dispose of hazardous waste. This process is used to avoid the dangers of combustion and is preferable when dealing with PCBs, organic waste and pesticides.
Disposing in a landfill: A landfill is a disposal facility where rubbish is placed in. Land treatment facilities are not landfills.
LIQUID WASTE
Liquid waste is commonly found both in households as well as in industries. This waste includes dirty water, organic liquids, wash water, waste detergents and even rainwater.
You should also know that liquid waste can be classified into point and non-point source waste. All manufactured liquid waste is classified as point source waste. On the other hand, natural liquid waste is classified as non-point source waste.
Glossary
Incinerate:
destroy (something, especially waste material) by burning.
By undefined
10 notes ・ 4 views
English
Upper Intermediate