Dec 27, 2022
VERB TENSES
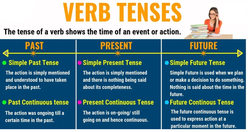
In the English language, tenses play an important role in sentence formation. The tense of a verb shows the time of an event or action.
The concept of time can be split into:
The Present: What you are currently doing.
* I eat. – I am eating.
* She goes to school. – She is going to school.
The Past: What you did some time back.
* I ate. – I was eating.
* She went to school. – She was going to school.
The Future: What you will do later.
* I will eat. – I will be eating
* She will go to school.
Types of Tenses
There are four types of verb tenses. Simple, Perfect, Continuous and Present Perfect Continuous and each of these has a present, past and future form.
Present Tense
Simple Present Tense
In Simple Present, the action is simply mentioned and there is nothing being said about its completeness.
Simple Present Tense
A simple Present Tense is a verb form of a sentence that tells about the action, circumstance which happens regularly, or occurrences.
The simple present tense is used to talk about general things, and not only the present situation.
It is used to tell what happens sometimes, all the time, or which is true. The simple present tense is also used when we used to say or suggest something.
For example:
I eat.
I sleep.

The Structures of Simple Present Tense
POSITIVE FORMS (+) :
Subject ( I, You, We, They ) + V1 ( First Form of Verb )
Subject ( He, She, It ) + VERB – S / ES / IES
NEGATIVE FORMS (-) :
Subject ( I, You, We, They ) + do not / don’t + V1 ( First Form of Verb )
Subject ( He, She, It ) + does not / doesn’t + V1 ( First Form of Verb )
QUESTION FORMS (?) :
Do + Subject ( I, You, We, They ) + V1 ( First Form of Verb )
Does + Subject ( He, She, It ) + V1 ( First Form of Verb )
SHORT ANSWER FORMS ( + / – ) :
YES / NO + Subject ( I, You, We, They )+ do / do not (don’t)
YES / NO + Subject ( He, She, It ) + does / does not (doesn’t)
ATTENTION:
1. In Simple Present Tense, we add the suffix -s at the end of the verbs for the third singular subject ( He, She, It ). On the other hand, we use first forms of the verbs for other subjects ( I, You, We, You, They).
2. Although we add the suffix -s at the end of the verb for the third singular subjects in positive sentences, we remove the suffix -s at the end of the verb in questions and negative sentences because of being used ‘does’ or ‘doesn’t’ as an auxillary verb.
Sentence Structure Rules
Structurally, the simple present tense can be written in this format.
Positive statements
[Subject + verb (s/es) + object]
Negative statements
[Subject + do/does + not + verb + object]
Question statements
[Do/does + subject + verb + object + ?]
Positive Sentences ( Sbj + V1 /V(-s,-es,-ies) )
Examples:
My mother lets me go out with my friends.
I prefer my coffee black.
She puts the keys on the table.
The teacher shouts at us all the time.
I have two brothers.
Coffee grows in Brazil.
Negative Sentences ( Sbj + do/does not + V1)
Examples:
My mother does not (doesn’t) let me go out with my friends.
I do not (don’t) prefer my coffee black.
She does not (doesn’t) put the keys on the table.
The teacher does not (doesn’t) shout at us all the time.
I do not (don’t) have two brothers.
Coffee does not (doesn’t) grow in Brazil.
Question Sentences ( Do/Does + Sbj + V1)
Examples:
Does your mother let you go out with your friends?
Do you prefer your coffee black?
Does she put the keys on the table?
Does the teacher shout at us all the time?
Do I have two brothers?
Does coffee grow in Brazil?
Examples of Present Simple Tense in Sentence
1. He plays the piano. (positive)
2. He does not play the piano. (negative)
3. Does he play the piano? (question)
4, Romie loves to eat burgers. (positive)
5. Romie does not love to eat burgers. (negative)
6. Does Romie love to eat burgers? (question)
7. We produce biogas from manure. (positive)
8. We do not produce biogas from manure. (negative)
9. Do we produce biogas from manure? (question)
10. I come from Paris. (positive)
11. I do not come to Paris. (negative)
12. Do I come to Paris? (question)
Exercise of Present Simple Tense
Complete the following sentence by using the appropriate verbs.
( believe, play, eat, need, cause, held, open, write, live, revolve )
1. Anthony _______ a letter.
2. I never _______ bananas.
3. The theatre _______ at 9 o’clock.
4. Damaged roads _________ many road accidents.
5. The cricket world cup ________ place every four years.
6. His elder brother _______ in Chicago.
7. She ________ in God.
8. The Earth __________ around the Sun.
9. Wheat ________ medium water to grow in farmland.
10. They ________ basketball games daily.
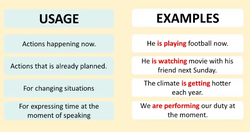
The present continuous tense is used for actions happening now or for an action that is unfinished. This tense is also used when the action is temporary.
How to Form the Present Continuous Tense
The present continuous tense is formed with the subject plus the present particle form (-ing) of the main verb and the present continuous tense of the verb to be: am, is, are.
One simple example of this tense is: He is swimming. "He" is the subject, "is" is the present tense of the verb to be and "swimming" is the present participle verb form. Some other forms of this verb tense are:
I am singing at church today.
The boys are playing ball after school.
Examples of the Present Continuous Tense
The following are basic examples of the present continuous tense. The verb tense in each sentence is underlined.
She is crying.
He is talking to his friend.
The baby is sleeping in his crib.
We are visiting the museum in the afternoon.
Present continuous tense can be used to express something happening right now or to express something that is not happening right now. Examples of this use include:
He is not standing.
Anthony is sitting in the chair.
You are not watching the movie.
Rose is reading a book.
Present continuous tense can also be used to show that something will or will not happen in the near future. Examples of this use include:
She is not going to the game tonight.
He is meeting his friends after school.
Are you visiting your cousin this weekend?
I am not going to the meeting after work.
Is John playing football today?
Present continuous tense can be used for actions that are still happening at the time of speaking. Examples of this use include:
Marc is making pizza now.
They are eating lunch right now.
Frances is talking on the phone at the moment.
Present continuous tense can be used in questions as well. Here are some more examples of this use:
Is she laughing?
Are they listening to the teacher?
Is the baby drinking his bottle?
Are you going?
More Uses of Present Continuous Tense
In addition to the above, the present continuous tense can be used to describe actions that are being repeated. Words like always, constantly and forever are used along with the verb. Examples of this use include:
Jack and Jill are always fighting.
She is constantly complaining about her sister.
Her mother is forever misplacing her keys.
Present continuous tense can be used when speaking about current trends. Examples of this use include:
Shopping online is growing in popularity nowadays.
The stocks are dropping constantly due to the economy.
Today, most people are using text messages instead of the phone.
Another use of this tense is when talking about a planned event in the future. Examples of this use include:
We are leaving for the beach tomorrow morning.
The kids are arriving at six o'clock.
She is speaking at the conference this evening.
When Not to Use Present Continuous Tense
There are certain verbs that cannot be used in the present continuous tense. The following verbs are non-continuous:
Communication: agree, promise, surprise
Feelings: like, love, hate
Senses: hear, see, smell, taste
Thinking: believe, know, understand
The Importance of Present Continuous Tense
As you can see the present continuous tense is most often used in English grammar to describe a continuing action, something that in unfinished. This tense is also important since it is a simple sentence structure that can show actions or events that are happening right now, in the planned future, or sometimes even in the past.
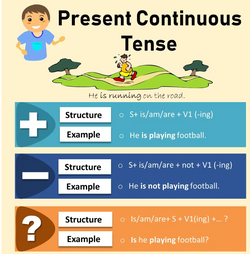
Present continuous tense (Present progressive tense)
Signal Words
at the moment
just now
right now
Structure / Formula
Subject + is/am/are + Present participle (-ing) for
Subject (I) am Present participle(-ing)+…
Subject (He/she/it) is Present participle(-ing)+…
Subject (We/They) are Present participle(-ing)+…
Positive Sentences
To make the positive sentences, we use the same structure,
Subject + is/am/are + Present participle (-ing) form
Examples of positive sentences
Julia is making a sponge cake right now.
He is going to the hill station next week.
Negative Sentences
We add ‘not’ after auxiliary verb to make the sentence negative.
Subject + is/am/are + not + Present participle (-ing) form
Examples of negative sentences.
Julia is not making a sponge cake right now.
He is not going to hill station next week.
Examples of question sentences.
Is Julia making a sponge cake right now?
Is he going to hill station next week?
By undefined
31 notes ・ 28 views
English
Beginner