Oct 31, 2023
The Atomic Habit #4
5. The Best Way to Start a New Habit
In 2001, RESEARCHERS in Great Britain began working with 248 people to build better exercise habits over the course of two weeks. The subjects were divided into three groups.
The first group was the control group. They were simply asked to track how often they exercised.
The second group was the “motivation” group. They were asked not only to track their workouts but also to read some material on the benefits of exercise. The researchers also explained to the group how exercise could reduce the risk of coronary heart disease and improve heart health.
Finally, there was the third group. These subjects received the same presentation as the second group, which ensured that they had equal levels of motivation. However, they were also asked to formulate a plan for when and where they would exercise over the following week. Specifically, each member of the third group completed the following sentence: “During the next week, I will partake in at least 20 minutes of vigorous exercise on [DAY] at [TIME] in [PLACE].”
5. The Best Way to Start a New Habit
In the first and second groups, 35 to 38 percent of people exercised at least once per week. (Interestingly, the motivational presentation given to the second group seemed to have no meaningful impact on behavior.) But 91 percent of the third group exercised at least once per week—more than
double the normal rate.
The sentence they filled out is what researchers refer to as an
implementation intention, which is a plan you make beforehand about when and where to act. That is, how you intend to implement a particular habit.
The cues that can trigger a habit come in a wide range of form —the feel of your phone buzzing in your pocket, the smell of chocolate chip cookies, the sound of ambulance sirens—but the two most common cues are time and location. Implementation intentions leverage both of these cues.
5. The Best Way to Start a New Habit
Broadly speaking, the format for creating an implementation
intention is:
“When situation X arises, I will perform response Y.”
Hundreds of studies have shown that implementation intentions are effective for sticking to our goals, whether it’s writing down the exact time and date of when you will get a flu shot or recording the time of your colonoscopy appointment. They increase the odds that people will stick
with habits like recycling, studying, going to sleep early, and stopping smoking.
Researchers have even found that voter turnout increases when people are forced to create implementation intentions by answering questions like:
“What route are you taking to the polling station? At what time are you planning to go? What bus will get you there?”
Other successful government programs have prompted citizens to make a clear plan to send taxes in on time or provided directions on when and where to pay late traffic bills. The punch line is clear: people who make a specific plan for when and where they will perform a new habit are more likely to follow through. Too many people try to change their habits without these basic details figured out. We tell ourselves, “I’m going to eat healthier” or “I’m going to write
more,” but we never say when and where these habits are going to happen. We leave it up to chance and hope that we will “just remember to do it” or feel motivated at the right time. An implementation intention sweeps away foggy notions like “I want to work out more” or “I want to be more
productive” or “I should vote” and transforms them into a concrete plan of action.
Many people think they lack motivation when what they really lack is clarity. It is not always obvious when and where to take action. Some people spend their entire lives waiting for the time to be right to make an improvement. Once an implementation intention has been set, you don’t have to wait for inspiration to strike. Do I write a chapter today or not? Do I meditate this morning or at lunch? When the moment of action occurs, there is no need to make a decision. Simply follow your predetermined plan.
The simple way to apply this strategy to your habits is to fill out this sentence:
I will [BEHAVIOR] at [TIME] in [LOCATION].
Meditation. I will meditate for one minute at 7 a.m. in my kitchen.
Studying. I will study Spanish for twenty minutes at 6 p.m. in my bedroom.
Exercise. I will exercise for one hour at 5 p.m. in my local gym.
Marriage. I will make my partner a cup of tea at 8 a.m. in the kitchen.
If you aren’t sure when to start your habit, try the first day of the week, month, or year. People are more likely to take action at those times because hope is usually higher. If we have hope, we have a reason to take action. A fresh start feels motivating.
There is another benefit to implementation intentions. Being specific about what you want and how you will achieve it helps you say no to things that derail progress, distract your attention, and pull you off course. We often say yes to little requests because we are not clear enough about what we need to be doing instead. When your dreams are vague, it’s easy to rationalize little exceptions all day long and never get around to the specific things you need to do to succeed.
Give your habits a time and a space to live in the world. The goal is to make the time and location so obvious that, with enough repetition, you get an urge to do the right thing at the right time, even if you can’t say why. As the writer Jason Zweig noted, “Obviously you’re never going to just work
out without conscious thought. But like a dog salivating at a bell, maybe you start to get antsy around the time of day you normally work out.” There are many ways to use implementation intentions in your life and work. My favorite approach is one I learned from Stanford professor BJ Fogg and it is a strategy I refer to as habit stacking.
HABIT STACKING: A SIMPLE PLAN TO OVERHAUL YOUR HABITS
The French philosopher Denis Diderot lived nearly his entire life in poverty, but that all changed one day in 1765.
Diderot’s daughter was about to be married and he could not afford to pay for the wedding. Despite his lack of wealth, Diderot was well known for his role as the co-founder and writer of Encyclopédie, one of the most comprehensive encyclopedias of the time. When Catherine the Great, the
Empress of Russia, heard of Diderot’s financial troubles, her heart went out to him. She was a book lover and greatly enjoyed his encyclopedia. She offered to buy Diderot’s personal library for £1,000—more than $150,000
today.* Suddenly, Diderot had money to spare. With his new wealth, he not only paid for the wedding but also acquired a scarlet robe for himself. Diderot’s scarlet robe was beautiful. So beautiful, in fact, that he immediately noticed how out of place it seemed when surrounded by his more common possessions. He wrote that there was “no more coordination,
no more unity, no more beauty” between his elegant robe and the rest of his stuff.
Diderot soon felt the urge to upgrade his possessions. He replaced his rug with one from Damascus. He decorated his home with expensive sculptures. He bought a mirror to place above the mantel, and a better kitchen table. He tossed aside his old straw chair for a leather one. Like falling dominoes, one purchase led to the next. Diderot’s behavior is not uncommon. In fact, the tendency for one purchase to lead to another one has a name: the Diderot Effect. The Diderot
Effect states that obtaining a new possession often creates a spiral of consumption that leads to additional purchases.
You can spot this pattern everywhere. You buy a dress and have to get new shoes and earrings to match. You buy a couch and suddenly question the layout of your entire living room. You buy a toy for your child and soon find yourself purchasing all of the accessories that go with it. It’s a chain
reaction of purchases. Many human behaviors follow this cycle. You often decide what to do next based on what you have just finished doing. Going to the bathroom
leads to washing and drying your hands, which reminds you that you need to put the dirty towels in the laundry, so you add laundry detergent to the shopping list, and so on. No behavior happens in isolation. Each action becomes a cue that triggers the next behavior.
HABIT STACKING: A SIMPLE PLAN TO OVERHAUL YOUR HABITS
Why is this important?
When it comes to building new habits, you can use the connectedness of behavior to your advantage. One of the best ways to build a new habit is to identify a current habit you already do each day and then stack your new behavior on top. This is called habit stacking.
Habit stacking is a special form of an implementation intention. Rather than pairing your new habit with a particular time and location, you pair it with a current habit. This method, which was created by BJ Fogg as part of his Tiny Habits program, can be used to design an obvious cue for nearly any habit.*
The habit stacking formula is:
“After [CURRENT HABIT], I will [NEW HABIT].”
For example:
Meditation. After I pour my cup of coffee each morning, I will meditate for one minute.
Exercise. After I take off my work shoes, I will immediately change into my workout clothes.
Gratitude. After I sit down to dinner, I will say one thing I’m grateful for that happened today.
Marriage. After I get into bed at night, I will give my partner a kiss.
Safety. After I put on my running shoes, I will text a friend or family member where I am running and how long it will take.
The key is to tie your desired behavior into something you already do each day. Once you have mastered this basic structure, you can begin to create larger stacks by chaining small habits together. This allows you to take advantage of the natural momentum that comes from one behavior leading into the next—a positive version of the Diderot Effect.
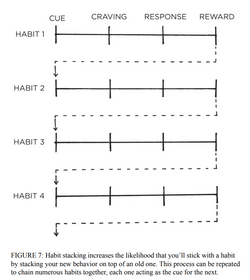
HABIT STACKING
Your morning routine habit stack might look like this:
1. After I pour my morning cup of coffee, I will meditate for sixty seconds.
2. After I meditate for sixty seconds, I will write my to-do list for the day.
3. After I write my to-do list for the day, I will immediately begin my first task.
Or, consider this habit stack in the evening
1. After I finish eating dinner, I will put my plate directly into the dishwasher.
2. After I put my dishes away, I will immediately wipe down the counter.
3. After I wipe down the counter, I will set out my coffee mug for
tomorrow morning.
You can also insert new behaviors into the middle of your current routines. For example, you may already have a morning routine that looks like this: Wake up > Make my bed > Take a shower. Let’s say you want to develop the habit of reading more each night. You can expand your habit stack and try something like: Wake up > Make my bed > Place a book on my pillow > Take a shower. Now, when you climb into bed each night, a book will be sitting there waiting for you to enjoy.
Overall, habit stacking allows you to create a set of simple rules that guide your future behavior. It’s like you always have a game plan for which action should come next. Once you get comfortable with this approach, you can develop general habit stacks to guide you whenever the situation is appropriate:
- Exercise. When I see a set of stairs, I will take them instead of using the elevator.
- Social skills. When I walk into a party, I will introduce myself to someone I don’t know yet.
- Finances. When I want to buy something over $100, I will wait twenty-four hours before purchasing.
- Healthy eating. When I serve myself a meal, I will always put veggies on my plate first.
- Minimalism. When I buy a new item, I will give something away. (“One in, one out.”)
- Mood. When the phone rings, I will take one deep breath and smile before answering.
- Forgetfulness. When I leave a public place, I will check the table and chairs to make sure I don’t leave anything behind
No matter how you use this strategy, the secret to creating a successful habit stack is selecting the right cue to kick things off. Unlike an implementation intention, which specifically states the time and location for a given behavior, habit stacking implicitly has the time and location built into it. When and where you choose to insert a habit into your daily routine can make a big difference. If you’re trying to add meditation into your morning routine but mornings are chaotic and your kids keep running into
the room, then that may be the wrong place and time. Consider when you are most likely to be successful. Don’t ask yourself to do a habit when you’re likely to be occupied with something else.
Your cue should also have the same frequency as your desired habit. If you want to do a habit every day, but you stack it on top of a habit that only happens on Mondays, that’s not a good choice.
One way to find the right trigger for your habit stack is by brainstorming a list of your current habits. You can use your Habits Scorecard from the last chapter as a starting point. Alternatively, you can create a list with two columns. In the first column, write down the habits you do each day without
fail.*
For example:
Get out of bed.
Take a shower.
Brush your teeth.
Get dressed.
Brew a cup of coffee.
Eat breakfast.
Take the kids to school.
Start the work day.
Eat lunch.
End the work day.
Change out of work clothes.
Sit down for dinner.
Turn off the lights.
Get into bed
Your list can be much longer, but you get the idea. In the second column, write down all of the things that happen to you each day without fail. For example:
The sun rises.
You get a text message.
The song you are listening to ends.
The sun sets.
Armed with these two lists, you can begin searching for the best place to layer your new habit into your lifestyle. Habit stacking works best when the cue is highly specific and immediately actionable. Many people select cues that are too vague. I made this mistake myself. When I wanted to start a push-up habit, my habit stack was “When I take a break for lunch, I will do ten push-ups.” At first glance, this sounded reasonable. But soon, I realized the trigger was unclear.
Would I do my push-ups before I ate lunch? After I ate lunch? Where would I do them? After a few inconsistent days, I changed my habit stack to: “When I close my laptop for lunch, I will do ten push-ups next to my desk.” Ambiguity gone.
Habits like “read more” or “eat better” are worthy causes, but these goals do not provide instruction on how and when to act. Be specific and clear:
After I close the door. After I brush my teeth. After I sit down at the table.
The specificity is important. The more tightly bound your new habit is to a specific cue, the better the odds are that you will notice when the time comes to act.
The 1st Law of Behavior Change is to make it obvious. Strategies like implementation intentions and habit stacking are among the most practical ways to create obvious cues for your habits and design a clear plan for when and where to take action.
CHAPTER SUMMARY
- The 1st Law of Behavior Change is make it obvious.
- The two most common cues are time and location.
- Creating an implementation intention is a strategy you can use to pair a new habit with a specific time and location.
- The implementation intention formula is: I will [BEHAVIOR] at
[TIME] in [LOCATION].
- Habit stacking is a strategy you can use to pair a new habit with a current habit.
- The habit stacking formula is: After [CURRENT HABIT], I will
[NEW HABIT]
Motivation Is Overrated; Environment Often Matters More.
ANNE THORNDIKE, A primary care physician at Massachusetts General Hospital in Boston, had a crazy idea. She believed she could improve the eating habits of thousands of hospital staff and visitors without changing
their willpower or motivation in the slightest way. In fact, she didn’t plan on talking to them at all.
Thorndike and her colleagues designed a six-month study to alter the “choice architecture” of the hospital cafeteria. They started by changing how drinks were arranged in the room. Originally, the refrigerators located next to the cash registers in the cafeteria were filled with only soda. The researchers added water as an option to each one. Additionally, they placed baskets of bottled water next to the food stations throughout the room. Soda was still in the primary refrigerators, but water was now available at all drink locations.
Over the next three months, the number of soda sales at the hospital dropped by 11.4 percent. Meanwhile, sales of bottled water increased by 25.8 percent. They made similar adjustments—and saw similar results— with the food in the cafeteria. Nobody had said a word to anyone eating there.
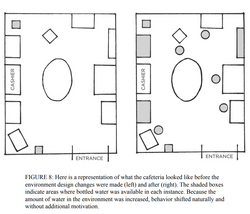
People often choose products not because of what they are, but because of where they are. If I walk into the kitchen and see a plate of cookies on the counter, I’ll pick up half a dozen and start eating, even if I hadn’t been thinking about them beforehand and didn’t necessarily feel hungry. If the communal table at the office is always filled with doughnuts and bagels, it’s going to be hard not to grab one every now and then. Your habits change depending on the room you are in and the cues in front of you.
Environment is the invisible hand that shapes human behavior. Despite our unique personalities, certain behaviors tend to arise again and again under certain environmental conditions. In church, people tend to talk in whispers. On a dark street, people act wary and guarded. In this way, the most common form of change is not internal, but external: we are changed by the world around us. Every habit is context dependent.
In 1936, psychologist Kurt Lewin wrote a simple equation that makes a powerful statement: Behavior is a function of the Person in their Environment, or B = f (P,E).
It didn’t take long for Lewin’s Equation to be tested in business. In 1952, the economist Hawkins Stern described a phenomenon he called Suggestion Impulse Buying, which “is triggered when a shopper sees a product for the first time and visualizes a need for it.” In other words, customers will occasionally buy products not because they want them but because of how they are presented to them.
For example, items at eye level tend to be purchased more than those down near the floor. For this reason, you’ll find expensive brand names featured in easy-to-reach locations on store shelves because they drive the most profit, while cheaper alternatives are tucked away in harder-to-reach spots. The same goes for end caps, which are the units at the end of aisles. End caps are moneymaking machines for retailers because they are obvious locations that encounter a lot of foot traffic. For example, 45 percent of Coca-Cola sales come specifically from end-of-the-aisle racks.
The more obviously available a product or service is, the more likely you are to try it. People drink Bud Light because it is in every bar and visit Starbucks because it is on every corner. We like to think that we are in control. If we choose water over soda, we assume it is because we wanted to do so. The truth, however, is that many of the actions we take each day are shaped not by purposeful drive and choice but by the most obvious option.
Every living being has its own methods for sensing and understanding the world. Eagles have remarkable long-distance vision. Snakes can smell by “tasting the air” with their highly sensitive tongues. Sharks can detect small amounts of electricity and vibrations in the water caused by nearby fish. Even bacteria have chemoreceptors—tiny sensory cells that allow them to detect toxic chemicals in their environment.
In humans, perception is directed by the sensory nervous system. We perceive the world through sight, sound, smell, touch, and taste. But we also have other ways of sensing stimuli. Some are conscious, but many are nonconscious. For instance, you can “notice” when the temperature drops before a storm, or when the pain in your gut rises during a stomachache, or when you fall off balance while walking on rocky ground. Receptors in your body pick up on a wide range of internal stimuli, such as the amount of salt in your blood or the need to drink when thirsty.
The most powerful of all human sensory abilities, however, is vision. The human body has about eleven million sensory receptors. Approximately ten million of those are dedicated to sight. Some experts estimate that half of the brain’s resources are used on vision. Given that we are more dependent on vision than on any other sense, it should come as no surprise that visual cues are the greatest catalyst of our behavior. For this
reason, a small change in what you see can lead to a big shift in what you do. As a result, you can imagine how important it is to live and work in environments that are filled with productive cues and devoid of unproductive ones.
Thankfully, there is good news in this respect. You don’t have to be the victim of your environment. You can also be the architect of it.
Glossary
Overrated: rated or valued too highly.
A primary care physician (PCP), or primary care provider, is a health care professional who practices general medicine.
Alter: change
communal table: Also called “community tables,” communal tables are large tables in restaurants that seat more than one party at a time.
every now and then: it happens sometimes but not very often or regularly.
wary: feeling or showing caution about possible dangers or problems.
guarded:
cautious and having possible reservations.
End-caps: a rack or counter at the end of a store aisle used to display promotional or sale items.
Chemoreceptors: a sense organ (such as a taste bud) responding to chemical stimuli.
gut: stomach, belly, intestine
HOW TO DESIGN YOUR ENVIRONMENT FOR SUCCESS
During the energy crisis and oil embargo of the 1970s, Dutch researchers began to pay close attention to the country’s energy usage. In one suburb near Amsterdam, they found that some homeowners used 30 percent less energy than their neighbors—despite the homes being of similar size and getting electricity for the same price.
It turned out the houses in this neighborhood were nearly identical except for one feature: the location of the electrical meter. Some had one in the basement. Others had the electrical meter upstairs in the main hallway. As you may guess, the homes with the meters located in the main hallway used less electricity. When their energy use was obvious and easy to track, people changed their behavior.
HOW TO DESIGN YOUR ENVIRONMENT FOR SUCCESS
Every habit is initiated by a cue, and we are more likely to notice cues that stand out. Unfortunately, the environments where we live and work often make it easy not to do certain actions because there is no obvious cue to trigger the behavior. It’s easy not to practice the guitar when it’s tucked away in the closet. It’s easy not to read a book when the bookshelf is in the corner of the guest room. It’s easy not to take your vitamins when they are
out of sight in the pantry. When the cues that spark a habit are subtle or hidden, they are easy to ignore.
By comparison, creating obvious visual cues can draw your attention toward a desired habit. In the early 1990s, the cleaning staff at Schiphol Airport in Amsterdam installed a small sticker that looked like a fly near the center of each urinal. Apparently, when men stepped up to the urinals, they aimed for what they thought was a bug. The stickers improved their aim
and significantly reduced “spillage” around the urinals. Further analysis determined that the stickers cut bathroom cleaning costs by 8 percent per year.
HOW TO DESIGN YOUR ENVIRONMENT FOR SUCCESS
I’ve experienced the power of obvious cues in my own life. I used to buy apples from the store, put them in the crisper in the bottom of the refrigerator, and forget all about them. By the time I remembered, the apples would have gone bad. I never saw them, so I never ate them.
Eventually, I took my own advice and redesigned my environment. I bought a large display bowl and placed it in the middle of the kitchen counter. The next time I bought apples, that was where they went—out in the open where I could see them. Almost like magic, I began eating a few apples each day simply because they were obvious rather than out of sight.
Here are a few ways you can redesign your environment and make the cues for your preferred habits more obvious:
If you want to remember to take your medication each night, put your pill bottle directly next to the faucet on the bathroom counter.
- If you want to practice guitar more frequently, place your guitar stand in the middle of the living room.
- If you want to remember to send more thank-you notes, keep a stack of stationery on your desk.
- If you want to drink more water, fill up a few water bottles each morning and place them in common locations around the house.
HOW TO DESIGN YOUR ENVIRONMENT FOR SUCCESS
If you want to make a habit a big part of your life, make the cue a big part of your environment. The most persistent behaviors usually have multiple cues. Consider how many different ways a smoker could be prompted to pull out a cigarette: driving in the car, seeing a friend smoke, feeling stressed at work, and so on.
The same strategy can be employed for good habits. By sprinkling triggers throughout your surroundings, you increase the odds that you’ll think about your habit throughout the day. Make sure the best choice is the most obvious one. Making a better decision is easy and natural when the cues for good habits are right in front of you.
Environment design is powerful not only because it influences how we engage with the world but also because we rarely do it. Most people live in a world others have created for them. But you can alter the spaces where you live and work to increase your exposure to positive cues and reduce your exposure to negative ones. Environment design allows you to take back control and become the architect of your life. Be the designer of your world and not merely the consumer of it.
Glossary
Embargo: Prohibition, limitation of usage
Subtle: Unseen, not clear, soft
Crisper: Drawer in the fridge that helps fruits stays crips
THE CONTEXT IS THE CUE
The cues that trigger a habit can start out very specific, but over time your habits become associated not with a single trigger but with the entire context surrounding the behavior.
For example, many people drink more in social situations than they would ever drink alone. The trigger is rarely a single cue, but rather the
whole situation: watching your friends order drinks, hearing the music at the bar, seeing the beers on tap.
We mentally assign our habits to the locations in which they occur: the home, the office, the gym. Each location develops a connection to certain habits and routines. You establish a particular relationship with the objects on your desk, the items on your kitchen counter, the things in your bedroom.
THE CONTEXT IS THE CUE
Our behavior is not defined by the objects in the environment but by our relationship to them. In fact, this is a useful way to think about the influence of the environment on your behavior. Stop thinking about your environment as filled with objects. Start thinking about it as filled with relationships.
Think in terms of how you interact with the spaces around you. For one person, her couch is the place where she reads for an hour each night. For someone else, the couch is where he watches television and eats a bowl of ice cream after work. Different people can have different memories—and
thus different habits—associated with the same place.
The good news? You can train yourself to link a particular habit with a particular context. In one study, scientists instructed insomniacs to get into bed only when they were tired. If they couldn’t fall asleep, they were told to sit in a different room until they became sleepy. Over time, subjects began to associate the context of their bed with the action of sleeping, and it became
easier to quickly fall asleep when they climbed in bed. Their brains learned that sleeping—not browsing on their phones, not watching television, not staring at the clock—was the only action that happened in that room.
THE CONTEXT IS THE CUE
The power of context also reveals an important strategy: habits can be easier to change in a new environment. It helps to escape the subtle triggers and cues that nudge you toward your current habits. Go to a new place—a different coffee shop, a bench in the park, a corner of your room you seldom use—and create a new routine there.
It is easier to associate a new habit with a new context than to build a new habit in the face of competing cues. It can be difficult to go to bed early if you watch television in your bedroom each night. It can be hard to study in the living room without getting distracted if that’s where you always play video games. But when you step outside your normal environment, you leave your behavioral biases behind. You aren’t battling old environmental cues, which allows new habits to form without interruption.
Want to think more creatively? Move to a bigger room, a rooftop patio, or a building with expansive architecture. Take a break from the space where you do your daily work, which is also linked to your current thought patterns.
THE CONTEXT IS THE CUE
Trying to eat healthier? It is likely that you shop on autopilot at your regular supermarket. Try a new grocery store. You may find it easier to avoid unhealthy food when your brain doesn’t automatically know where it is located in the store.
When you can’t manage to get to an entirely new environment, redefine or rearrange your current one. Create a separate space for work, study, exercise, entertainment, and cooking. The mantra I find useful is “One space, one use.”
When I started my career as an entrepreneur, I would often work from my couch or at the kitchen table. In the evenings, I found it very difficult to stop working. There was no clear division between the end of work time and the beginning of personal time. Was the kitchen table my office or the space where I ate meals? Was the couch where I relaxed or where I sent emails? Everything happened in the same place.
THE CONTEXT IS THE CUE
A few years later, I could finally afford to move to a home with a separate room for my office. Suddenly, work was something that happened “in here” and personal life was something that happened “out there.” It was easier for me to turn off the professional side of my brain when there was a clear dividing line between work life and home life. Each room had one primary use. The kitchen was for cooking. The office was for working. Whenever possible, avoid mixing the context of one habit with another.
When you start mixing contexts, you’ll start mixing habits—and the easier ones will usually win out. This is one reason why the versatility of modern technology is both a strength and a weakness. You can use your phone for all sorts of tasks, which makes it a powerful device. But when you can use your phone to do nearly anything, it becomes hard to associate it with one
task. You want to be productive, but you’re also conditioned to browse social media, check email, and play video games whenever you open your phone. It’s a mishmash of cues.
THE CONTEXT IS THE CUE
You may be thinking, “You don’t understand. I live in New York City. My apartment is the size of a smartphone. I need each room to play multiple roles.” Fair enough. If your space is limited, divide your room into activity zones: a chair for reading, a desk for writing, a table for eating. You can do the same with your digital spaces. I know a writer who uses his computer only for writing, his tablet only for reading, and his phone only for social
media and texting. Every habit should have a home.
If you can manage to stick with this strategy, each context will become associated with a particular habit and mode of thought. Habits thrive under predictable circumstances like these. Focus comes automatically when you are sitting at your work desk. Relaxation is easier when you are in a space designed for that purpose. Sleep comes quickly when it is the only thing that happens in your bedroom. If you want behaviors that are stable and predictable, you need an environment that is stable and predictable.
A stable environment where everything has a place and a purpose is an environment where habits can easily form.
Chapter Summary
Small changes in context can lead to large changes in behavior over time.
Every habit is initiated by a cue. We are more likely to notice cues that stand out.
Make the cues of good habits obvious in your environment.
Gradually, your habits become associated not with a single trigger but with the entire context surrounding the behavior. The context becomes the cue.
It is easier to build new habits in a new environment because you are not fighting against old cues.



By undefined
34 notes ・ 173 views
English
Intermediate