Mar 9, 2022
grammar
arise arose arisen
awake awoke awoken
be was/were been
bear bore born(e)
beat beat beaten
become became become
begin began begun
bend bent bent
bet bet bet
bind bound bound
bite bit bitten
bleed bled bled
blow blew blown
break broke broken
breed bred bred
bring brought brought
broadcast broadcast broadcast
build built built
burn burnt/burned burnt/burned
burst burst burst
buy bought bought
can could … (been able)
catch caught caught
choose chose chosen
cling clung clung
come came come
cost cost cost
creep crept crept
cut cut cut
deal dealt dealt
dig dug dug
do did done
draw drew drawn
dream dreamt/dreamed dreamt/dreamed
drink drank drunk
drive drove driven
eat ate eaten
fall fell fallen
feed fed fed
feel felt felt
fight fought fought
find found found
fly flew flown
forbid forbade forbidden
forget forgot forgotten
forgive forgave forgiven
freeze froze frozen
get got got
give gave given
go went gone
grind ground ground
grow grew grown
hang hung hung
have had had
hear heard heard
hide hid hidden
hit hit hit
hold held held
hurt hurt hurt
keep kept kept
kneel knelt knelt
know knew known
lay laid laid
lead led led
lean leant/leaned leant/leaned
learn learnt/learned learnt/learned
leave left left
lend lent lent
lie (in bed) lay lain
lie (to not tell the truth) lied lied
light lit/lighted lit/lighted
lose lost lost
make made made
may might …
mean meant meant
meet met met
mow mowed mown/mowed
must had to …
overtake overtook overtaken
pay paid paid
put put put
read read read
ride rode ridden
ring rang rung
rise rose risen
run ran run
saw sawed sawn/sawed
say said said
see saw seen
sell sold sold
send sent sent
set set set
sew sewed sewn/sewed
shake shook shaken
shall should …
shed shed shed
shine shone shone
shoot shot shot
show showed shown
shrink shrank shrunk
shut shut shut
sing sang sung
sink sank sunk
sit sat sat
sleep slept slept
slide slid slid
smell smelt smelt
sow sowed sown/sowed
speak spoke spoken
spell spelt/spelled spelt/spelled
spend spent spent
spill spilt/spilled spilt/spilled
spit spat spat
spread spread spread
stand stood stood
steal stole stolen
stick stuck stuck
sting stung stung
stink stank stunk
strike struck struck
swear swore sworn
sweep swept swept
swell swelled swollen/swelled
swim swam swum
swing swung swung
take took taken
teach taught taught
tear tore torn
tell told told
think thought thought
throw threw thrown
understand understood understood
wake woke woken
wear wore worn
weep wept wept
will would …
win won won
wind wound wound
write wrote written
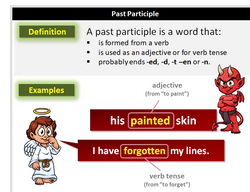
What Are Past Participles? (with Examples)
A past participle is a word that (1) is formed from a verb, (2) is used as an adjective or to form verb tense, and (3) probably ends with "-ed," "-d," "-t," "-en," or "-n." For example:
past participle examples
More Examples of the Present Perfect Tense
Here are some more examples of the present perfect tense:
The board has decided to uphold the appeal.
(This sentence carries the connotation that the board continues to uphold the appeal.)
I have taken the wrong path.
(Connotation: I am still on the wrong path.)
Comparing the Present Perfect Tense and the Simple Past Tense
Here is another example of the present perfect tense (highlighted).
For comparison, the example is given alongside similar-looking example featuring the simple past tense.
Janet has run two miles.
(This is the present perfect tense. In this example, Janet is still running when the words were said.)
Janet ran two miles.
(This is the simple past tense. In this example, Janet has stopped running when the words were said.)
Here is another example:
David has worked alongside two of the world's finest scientists in the field of entomology.
(This is the present perfect tense. In this example, David might have finished working with those scientists, but the sentence carries the connotation that he is still working as an entomologist.)
David worked alongside two of the world's finest scientists in the field of entomology.
(This is the simple past tense. This example carries the connotation that David no longer works as an entomologist.)
Forming the Present Perfect Tense
The present perfect tense is formed:
[subject] + "has" or "have" + [past participle]
I have worked.
She has painted.
The present perfect tense refers to an action or state that either occurred at an indefinite time in the past (e.g., we have talked before) or began in the past and continued to the present time (e.g., he has grown impatient over the last hour). This tense is formed by have/has + the past participle.
The construction of this verb tense is straightforward. The first element is have or has, depending on the subject the verb is conjugated with. The second element is the past participle of the verb, which is usually formed by adding -ed or -d to the verb’s root (e.g., walked, cleaned, typed, perambulated, jumped, laughed, sautéed) although English does have quite a few verbs that have irregular past participles (e.g., done, said, gone, known, won, thought, felt, eaten).
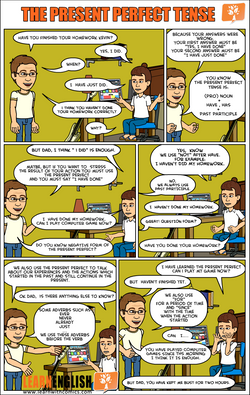
What Is the Present Perfect Tense? (with Examples)
The present perfect tense describes an action that began in the past (despite being a present tense). For example:
John has taken Sarah's advice.
They have fixed the fence.
Often, the action being described is still continuing into the present (e.g., John continues to take Sarah's advice). This is how the present perfect tense differs from the simple past tense.
The past simple tense is used to talk about things that both started and ended in the past. It is one of the most commonly used tenses in English as it indicates something that has already happened.
When to use the past simple tense
To talk about events that happened in the past —
I walked to school yesterday.
To talk about moods or states of being in the past —
I was a happy teenager.
To talk about repeated actions in the past —
I visited my grandma every winter for ten years.
Pro tip – Past simple is only used when the action or event in the past was completed.
If an action started in the past but is continuing into the future that is a different tense (present perfect).
1. Yesterday I ___________________ (forget) my dictionary at home; so, I
____________________(borrow) another one from my classmate.
2. I _____________________ (lose) my keys I can’t get in.
3. My brother ______________________ (visit) U.S. three times.
4. Last month I _______________________ (visit) Venice for the first time.
5. I _______________________ (know) Spanish when I was eight; but, by time I ___________
(forget).
6. My best friend Chris _______________________ (know) me for ten years, we still meet once
a week at least.
7. I ___________________ (play) volleyball since I was a little kid; I’m pretty good at it.
8. Tina __________________ (play) soccer at university, however she
__________________ (not / like) it.
9. Sorry, I __________________ (miss) the train; shall we meet tomorrow?
10. Yesterday was a tough day for me; first, I __________________ (miss) the bus; so, I
__________________ (not / reach) my meeting on time, and then I _______________ (miss)
the train; so, I was late home.
11. Last year I __________________ (go) to Paris.
12. I’m sorry, my mother isn’t here now. She __________________ (go) shopping.
13. Daniel __________________ (finish) his lunch quickly and left home.
14. I __________________ (finish) painting the walls finally and I’m so tired!
. I .................... with my son when you ....................
played, called
was playing, were calling
was playing, called
played, were calling
2. The doorbell .................... while I ..................... a bath.
rang, was having
was ringing, was having
was ringing. had
3. As I ........................ for bus, I ............................. Joe crossing the road.
waited, saw
was waiting, saw
waited, was seeing
4. Yesterday, I ....................... to the movies with my wife.
was going
went
had gone
5. When I was a child, we ................ our own amusements.
were making
made
have made
6. When we .................... home, we discovered that water .......................... down the walls.
reached, ran
reached, was running
was reaching, was running
7. It ........................ while I .......................... in Mumbai.
was happening, was living
happened, was living
happened, lived
8. I .................... in Rome for ten years while I ................. a child.
lived, was
was living, was
lived, had been
9. I ......................... all day yesterday.
had slept
was sleeping
10. What ................................. at 11 pm last night?
did you do
were you doing
had you done
11. Who .......................... you that watch?
was giving
gave
had given
12. When I ......................... into the office, everybody ...................
was walking
walked, worked
walked, was working
Yesterday I forgot my dictionary at home; so, I borrowed another one from my classmate.
2. I have lost my keys I can’t get in.
3. My brother has visited U.S. three times.
4. Last month I visited Venice for the first time.
5. I knew Spanish when I was eight; but, by time I forgot.
6. My best friend Chris has known me for ten years; we still meet once a week at least.
7. I have played volleyball since I was a little kid; I’m pretty good at it.
8. Tina played soccer at university, however she didn’t like it.
9. Sorry, I have missed the train; shall we meet tomorrow?
10. Yesterday was a tough day for me; first, I missed the bus; so, I didn’t reach my meeting on
time, and then I missed the train; so, I was late home.
11. Last year I went to Paris.
12. I’m sorry, my mother isn’t here now. She has gone shopping.
13. Daniel finished his lunch quickly and left home.
14. I have finished painting the walls finally and I’m so tired!
. I was playing with my son when you called.
2. The doorbell rang while I was having a bath.
3. As I was waiting for bus, I saw Joe crossing the road.
4. Yesterday, I went to the movies with my wife.
5. When I was a child, we made our own amusements.
6. When we reached home, we discovered that water was running down the walls.
7. It happened while I was working in Mumbai.
8. I lived in Rome for ten years while I was a child.
9. I was sleeping all day yesterday.
10. What were you doing at 11 pm last night?
11. Who gave you that watch?
12. When I walked into the office, everybody was working.
Definition of Past Continuous Tense
Past Continuous Tense is a tense which is used to indicate the actions or conditions that were happening at some point in time in the past but have now finished. In other words, past continuous tense is used to describe or indicate actions that began in the past and were continuing when another event occurred. It is important to note here that there may be two actions going on at the same time in the past, and one was interrupted by the happening of the other. Thus, both actions have occurred in the past. It is also known as the past progressive tense.
This tense uses was or were + present participle. In the forming of the past continuous tense, we use ‘was’ when the subject is Singular and ‘were’ when the subject is Plural. The second element that is the present participle is formed by adding -ing to the root of the verb.
For example, learning, studying, mixing, laughing, etc. While framing the questions using the past continuous tense, we indicate them by inverting the subject and was or were. For making negative sentences we use not.
Using Past Continuous Tense sentences to describe:
Following are the situations where we use Past Continuous Tense along with sentences:
For any interrupted action or condition in the past
Sentence: While she was cooking food, the microwave blew.
It means that she was cooking food in the past and the doorbell rang. So, the first event i.e. cooking got interrupted by the occurrence of the second event i.e. the blowing off of the microwave.
Interruption at a specific time
Sentence: Yesterday at 11 AM, I was having breakfast.
It means that at 11 AM I was in the process of having breakfast. I had started having breakfast earlier than 11 AM.
Describes parallel actions or events
Sentence: He was listening to music while walking in the garden.
It means that listening to music and walking was going on simultaneously or at the same time.
Describes Atmosphere
Sentence: When I reached the shopping mall, several people were busy buying clothes, children were playing in the gaming zone, and some were busy enjoying delicious food.
It expresses the atmosphere inside the shopping mall sometime in the past.
Use of ‘always’ and ‘constantly’
Sentence: He was constantly talking and irritated me.
It means that his constant talking in the past had irritated me then.