Feb 18, 2022
Beginner English Notebook
A. Context - What is it?
-Etymology: Latin word contextus meaning "to weave together"
- setting of a word or event
- words or sentences that surround the unknown word
Examples
1. Why did you graduate from School? Because, you passed all your exams
2. Why did you get married? Because you love your partner.
3. Why do you work at the Bank? Because, you are passionate about Accounting.
B. Importance
1. Tells us the time when an event is happening
2. Tells us about characters who are in the conversation or are part of the story
3. Tells us about the situation
C.How do we use context?
🕵️♂️Through context clues
1. An example of a word
To explain or illustrate.
Clue words: for example, for instance, including, such as
Passage:
Many people readily admit that they are hypochondriacs. For example, Travis once thought he had a flesh-eating virus when he found a mysterious red spot on his arm, and Kevin need only sneeze and he is convinced it is pnemonia.
2. A synonym (words that has the same meaning as another word)
An author/speaker can provide a similar meaning to the word you don't know.
Example
Katie always feel exhausted at the end of a long work day. She becomes too tired to move!
3. Antonym (words that mean the opposite of the given word)
The author/speaker explains a word by contrast or giving a difference.
Clue words: However, But, Yet, On the other hand, in contrast, unlike, while
Example
Martin is gregarious, unlike his brother who is quiet and shy.
4. Explanations/Cause and Effect
Sometimes, you have to read or hear the words surrounding the sentence to get an explanation of the unknown word.
Example
Jennifer begged her mom to let her go on the spring break trip and she was thrilled when her mom acquiesced.
We know the dog has a kind disposition because we’ve never seen her bite or scratch anyone.
During the demonstration, a skirmish broke out so the police were called to restore order
5. Morphology(Affixes - Prefixes and Suffixes)
Examples
Submarine -> Sub (Subway =Underground train ☆ Under transport) + Marine (Ocean + water) = Under water machine/vehicle
Reminder -> Re (repeat, re-do, restart) + Mind(think, use brain) + er ( person or thing that does or provides an action e.g. painter, manager, rice cooker, peeler) = a thing that prompts my mind to do something again
6. The topic or subject of the Text
Gives context to the words used in the passage/article.
7. Through pictures
Pictures can give the meaning behinds the words used in an image
B.Denotation and Connotation
📖Denotation is the actual definition of a word.
-Etymology : Latin "indication, act of indicating by a name
- means to denote, mark out
You’ve been looking up the denotation of words for MANY years now!! (Dictionary)
😊Connotation is the emotion that a word generates in addition to the actual meaning.
-Etymology: Latin "signify in addition to the main meaning"
- "to mark along with"
EXAMPLES
House: A building in which someone lives (neutral/definition) 📖Denotation
Home: A place of warmth, comfort and affection (positive)😊
Shanty: A small, crudely built shack. (negative)😡😢
C. Nuance
-Etymology: French "slight difference, shade of color" (refers to the different colors of the clouds)
-"slight or delicate degree of difference in expression, feeling, opinion, etc."
Nuances are tiny/subtle differences in the meaning of words, phrases or ideas
They can be found in:
1. Evaluative Adjectives
Words which express a positive or negative feeling e.g.
• Big-Extravangant-Humongous-Monstrous- Sizable
• Lovely-Fantastic-Great-Good-Tremendous
2. Modal verbs
A type of helping verb that shows possibility, intent, ability, necessity,permission, request, suggestions, order, obligation, or advice.
These are; can, will, may, might, must should, could and would.
Examples:
•I play guitar everyday -> I can play guitar everyday.
•It will rain today -> Judging by the clouds, it might rain today.
•I will go to the market today -> Will you go to the market today?
3. Adverbs of Possibility and Frequency
Possibility - give information about how something is like. Examples include; certainly, definitely, maybe, surely, clearly, obviously, perhaps, probably and undoubtedly.
Examples
• I will definitely call you tonight.
• Sarah will probably go to the park after school.
Sam obviously made a huge contribution to the success of the team.
Frequency - give information on how regularly or often something is done. Examples include: always, constantly, continually, frequently, infrequently, intermittently, normally, occasionally, often, periodically, rarely, regularly, seldom, sometimes.
Examples
•I always go to work on Monday morning.
•A sentence normally has a subject and verb.
• Paul rarely makes a mistake.
4. Synonyms
-words that have the same meaning
-each word brings with it its own connotations, feelings and potential uses.
For example, a building can serve as:
•A non-resident area - office, church, school, museum etc.
• A temporary residence area - hotel, inn,motel etc.
•A permanent/long term residence area - bungalow, condo, appartment, mansion et
ADJECTIVES 3
COMPARATIVE and SUPERLATIVE
We use comparative adjectives to compare two people, animals or things.
*New York is bigger than Madrid
*Sally is more beautiful than Pat
We use superlative adjectives to compare more than two people, animals or things
* Brazil is the largest country in South America
* Money isn't the most important thing in life
FORM
* ONE SYLLABLE :
COMPARATIVE - Adjective + -er + than - John is taller than Charles
SUPERLATIVE - the + adjective + -est - John is the tallest boy in the class
* TWO or MORE SYLLABLES
COMPARATIVE - More + adjective + than - Mary is more intelligent than Jane
SUPERLATIVE - the most + adjective - Mary is the most intelligent girl in the class
*IRREGULAR
good/well- better- the best
bad - worse - the worst
far - farther / further - the farthest / the furthest
little - less - the least
much - morr - the most
many- more - the most
SPELLING
*Adjectives of one syllable that end in -e: add -r / -st
large - larger - the largest
nice - nicer - the nicest
* Adjectives that end in a vowel + consonants -t, -d, -g, -m, -n : double the consonant and add -er/-est
fat - fatter - the fattest
slim – slimmer - the slimmest
big - bigger - the biggest
* Adjectives of two syllables that end in -y: change the -y to an -i and add -er / -est
busy – busier - the busiest
easy – easier - the easiest
early - earlier – the earliest
*Long words(2 / 3 / 4 syllables): add more / the most
modern - more modern - the most modern
beautiful - more beautiful - the most beautiful
expensive - more expensive - the most expensive
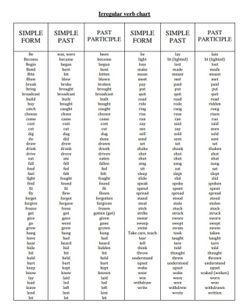
PAST PERFECT TENSE
Key word: Had
FORM
It is formed with the auxiliary(helping) verb "had" + past participle (-ed ending for regular verbs/different forms for irregular verbs)
😃Regular verbs
work -> worked
travel -> travelled
try -> tried
😂Irregular verbs
write -> written
make -> made
sing -> sung
POSITIVE/NEGATIVE/INTEROGATIVE SENTENCES
I had done, I had not done (I hadn't done) Had I done? Had I not done? (Hadn't I done?)
USE
1. We use the past perfect to make it clear that an action was completed before another action in the past.
Example
a. The door bell rang at last. I had been in the room since breakfast.
b. When I arrived there Sarah had already left.
c. I was so hungry! I had not eaten anything since the morning.
2. It is used to refer to an activity that was completed before a point of time in the past.
Example
a. In 2020 I had lived in the same place for ten years.
b. Had you ever travelled by plane before your holiday in Spain?
CONFUSIONS
😢Past perfect vs present perfect simple
1. The past perfect is often used with expressions indicating that the activity took some time, such as: for 10 years, since 1995, all week, all the time, always,
Examples
a. When the plane landed Tim had travelled all day.
b. My parents moved away from Paris. They had lived there since they got married.
c. In 2015 Derek started to work in Berlin. He had always planned it.
☆These expressions are also used with the present perfect.
☆The difference is, however, that the present perfect refers to events that started in the past and still continue, the past perfect expresses events that began before a point of time (or another action) in the past and continued to that point of time in the past.
❌I have been in Paris for a week.
(the present perfect - I came a week ago and I am still in Paris.)
✅When I met Anita I had been in Paris for a week.
(the past perfect - I came to Paris a week before I met Anita and I am not there anymore.)
2. We use the past perfect simple it does not always mean that an activity continued up to a point of time in the past. The event can end a long time before the point of time in the past that we refer to.
Example
In 2001 Angie worked in Glasgow. In 1980's she had worked in Wales.
(Angie left her job in Wales in 1989. In 2001 she worked in Glasgow. But we do not know what she did in the meantime.)
😢Past perfect vs past simple
1. The past simple is used for actions that happened some time ago/recently. The past perfect is used for actions that happened before a point of time in the past.
Example
a. Jim returned at 4 o'clock. He had called Jane on the way back home and now she appeared at the door.
(In this story the sentences are in a reversed order, because in reality, first Jim called Jane and then he returned. If we want to keep this sentence order, we must use the past perfect to make it clear that Jim called Jane first.)
✅ Jim had called Jane before he returned home at 4 o'clock. She appeared at the door when he arrived.
BUT if the sentence order is the same as the order of the events, we can use the past tense.
b. Jim called Jane on the way back home. He returned at 4 o'clock and now she appeared at the door.
☆This difference is important.
2. In some situations these two tenses have a completely different meaning.
Examples
◇ I arrived at the garage. They told me to pay in cash. But I only had my credit card. I couldn't pay. (In this case, I did not know that I had to pay in cash. They told me after my arrival.)
◇ I arrived at the garage. They had told me to pay in cash. I paid and left immediately. (In the second case I was informed before my arrival and had no problems.)
2.Past perfect tense and past simple are used differently in time clauses
☆We use the past tense if we want to express that the first action led to the second and that the second followed the first very closely.
Example
When the film ended he switched off the television.
The past perfect is used when we want to make it clear that the first action was completed before the second started and that there is no relation between them.
Example
When she had washed the dishes, she had a cup of tea. (Past perfect)
When she washed the dishes she put the plates in the cupboard. (Past simple)
But:
If we use "after"in a time clause the past perfect is much more usual/normal.
Examples
a. After she had washed the dishes, she had a cup of tea
b. After Ronaldo had scored the goal the fans went wild.
☆ We use the past perfect similarly with: as soon as, until, before, by the time, already.
b. He got up as soon as he had heard the alarm clock.
c. We did not stop until we had reached the coast.
d. Maria had finished her meal by the time I arrived.
d. Before she cut her hair she had consulted it.
e. Michael had already jogged by the time we ate.